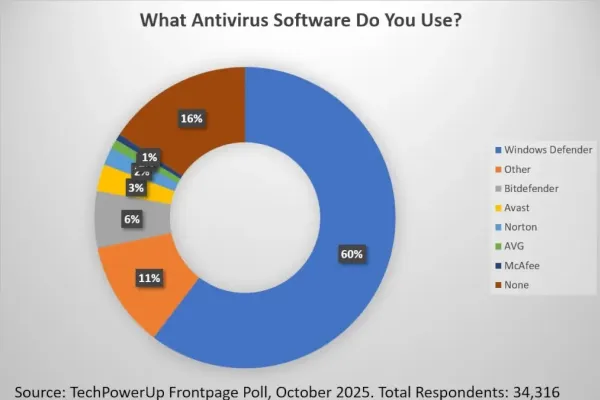
Today's digital landscape sees built-in antivirus tools offering substantial protection across major operating systems: Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu/Linux. These tools provide real-time scanning and malware detection, crucial for safeguarding against cyber threats.
Windows and macOS Protections
Microsoft Defender Antivirus comes with Windows 10 and 11, featuring real-time protection against viruses, spyware, ransomware, and phishing. It includes automatic updates, cloud-based scanning, and firewall settings. On macOS, XProtect, Gatekeeper, and the Malware Removal Tool (MRT) run by default. XProtect scans downloads, Gatekeeper limits app installs, and MRT removes detected malware. System Integrity Protection adds another security layer by preventing unauthorized system changes.
Ubuntu/Linux Security Features
Ubuntu relies on open-source architecture and user privilege models for enhanced security. Regular security patches keep the system robust. Tools like AppArmor enhance access control, while optional apps like ClamAV and UFW provide further antivirus scanning and firewall management. Users are encouraged to utilize trusted repositories and avoid running unverified scripts.
Best Practices and Recommendations
To maximize the effectiveness of built-in antivirus solutions, keep operating systems and applications updated. Avoid pirated software and suspicious links, use strong, unique passwords with a manager, and enable two-factor authentication. Backing up important data regularly is also advised. While built-in tools suffice for most, advanced users might consider third-party solutions for sandboxing, VPNs, and other enhanced security measures.