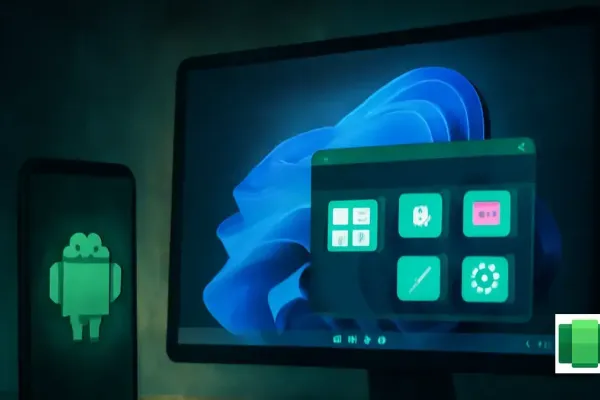
Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) enables users to run Android apps on Windows PCs, offering improved performance and accessibility for mobile applications that lack robust desktop versions.
Setup and Installation Process
To set up WSA, users must enable virtualization features: Hyper-V and the Virtual Machine Platform on Windows. Despite Microsoft ending official support in 2025, community builds continue thriving on platforms like GitHub. These versions can be installed via PowerShell by executing install.ps1 or using Run.bat.
- Enable virtualization features on Windows.
- Download a community WSA build from GitHub.
- Install WSA using PowerShell or Run.bat.
Managing and Installing Apps
After setup, users access the emulated device settings and WSA interface with tabs for System, Apps, and Advanced options. Google Play Store integration allows app installations and updates directly. For sideloading, enable Developer Options, use ADB with an IP address, and push APKs.
- Google Play Store integration for app updates.
- Enable Developer Options for APK sideloading.
- Connect using ADB with device IP.
User Experience and Control
Apps run in separate windows on Windows, launching from the Start menu, WSA apps, or the Play Store. Users manage these apps as regular Windows applications, including pinning and managing storage through App Settings.
- Apps have individual taskbar icons and window controls.
- Manage apps through App Settings.
- Community builds ensure ongoing viability.
The community-supported builds ensure WSA remains a viable option for running mobile apps on a desktop environment, despite the cessation of official Microsoft support.